Description
Since 2023, the oil market and energy policy in the Middle East have been continuously shaped by regional geopolitical tensions and shifts in the global economy. This period has been marked by increased volatility, directly reflected in oil price fluctuations and the strategic behavior of key players.
Current Dynamics of the Oil Market (2023–Present)
Since 2023, the global oil market has come under the influence of complex and multifaceted factors, leading to significant price volatility. While supply and demand remain the primary determinants, geopolitical tensions and broader economic trends play a decisive role in shaping current market conditions.
Demand Trends
Global demand for oil rose in 2023, reached record highs in 2024, and continues to grow in 2025, though at a slower pace.
- Economic Growth: The primary driver of demand remains global economic activity. Despite inflationary pressures and rising interest rates, economic growth—especially in developing countries—continues to sustain oil demand. China and India remain the main engines of consumption. While China occasionally faces economic challenges that temper demand, India’s consumption continues to grow steadily.
- Transport Sector: A significant portion of oil demand comes from the transportation sector. Increased consumption of automotive fuels (particularly in the U.S. during the summer season) and a rebound in air travel have supported high levels of oil use.
- Regional Disparities: Demand growth is uneven. While non-OECD countries are showing stable increases, demand in OECD countries is either flat or declining slightly.
Supply Trends
On the supply side, OPEC+ policy decisions and production levels in non-OPEC+ countries determine the market balance.
- OPEC+ Production Policy: The OPEC+ alliance, led by Saudi Arabia and Russia, actively manages market supply. In October 2023, the group implemented voluntary production cuts totaling 2.2 million barrels per day, aimed at stabilizing global prices amid recession concerns and high interest rates. These cuts were extended multiple times, including through the first quarter of 2024.
- Current Status (Mid-2025): OPEC+ has gradually begun phasing out its voluntary production cuts. Starting in April 2025, the alliance initiated modest production increases, which continued to expand from May through July. Additional significant increases are expected in August and September 2025. This strategy aims not only to support market balance but also to boost member states' revenues. Saudi Arabia continues to play its role as a “swing producer,” capable of rapidly adjusting output to meet market needs.
- Non-OPEC+ Production: The United States remains the world’s largest oil producer, maintaining record output levels. However, there are signs that U.S. shale oil production may be nearing a plateau. Other non-OPEC+ producers, such as Canada and Brazil, are also contributing significantly to global supply.
- Russian Oil: Despite Western sanctions, Russia has managed to reroute its oil exports—primarily to China and India. This has helped prevent a major supply shortfall on the global market, although the sanctions still affect Russia’s revenues and export logistics.
Geopolitical Factors and Price Volatility
Geopolitical tensions remain one of the primary drivers of oil price volatility.
- Israel-Hamas Conflict: Since October 2023, the ongoing conflict in the Gaza Strip has posed a persistent risk of regional escalation. Any expansion of hostilities—particularly involving Iran or its regional allies—adds a risk premium to oil prices, as investors fear potential supply disruptions.
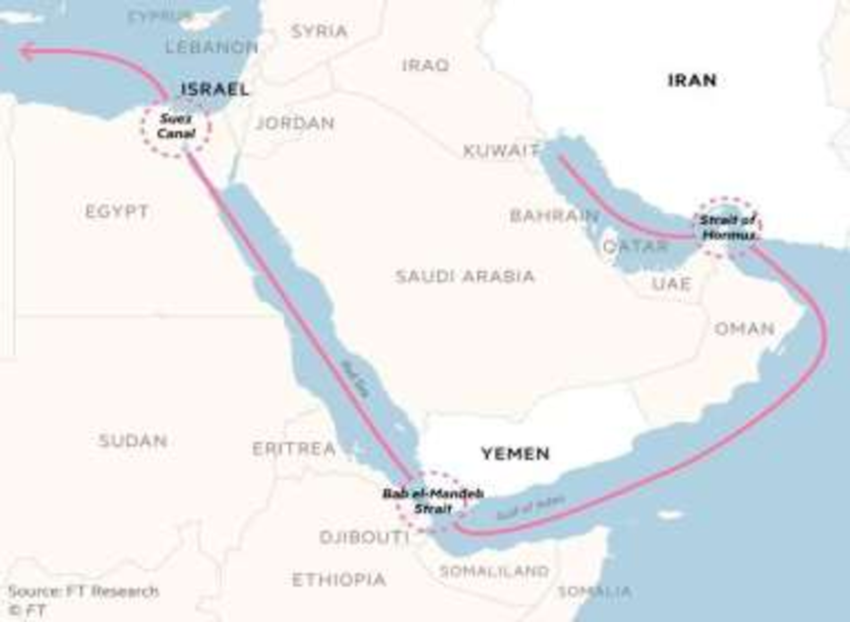
- Red Sea Crisis: The attacks on ships in the Red Sea by Yemeni Houthis (beginning in November 2023) have seriously disrupted maritime trade. Many shipping companies, including oil tanker operators, have been forced to reroute around the African continent via the Cape of Good Hope. This shift has led to increased transportation costs, higher fuel consumption, and rising insurance premiums—all of which exert upward pressure on oil prices, even in the absence of a large-scale supply shortage.
- Iran Sanctions: Ongoing sanctions related to Iran's nuclear program continue to generate uncertainty in the oil market. While Iran continues to export oil despite the sanctions, any change in its geopolitical status could significantly impact global supply dynamics.
Inventories and Future Outlook
One key indicator of market stability is the level of commercial oil inventories. As of May 2025, global oil stockpiles have increased—particularly in non-OECD countries and in oil currently in maritime transit. This suggests that, for now, supply is outpacing demand, easing some of the upward pressure on prices.
However, the medium- to long-term outlook remains uncertain. Slower global demand growth in 2025 and 2026—driven by economic challenges and the ongoing shift toward renewable energy—could lead to an oversupplied market, unless OPEC+ adjusts its production levels accordingly. At the same time, geopolitical risks continue to act as an unpredictable factor that could trigger sharp price swings at any moment.
Geopolitical Tension and Oil Price Fluctuations (2023–Present)
Since 2023, geopolitical instability in the Middle East has had a significant impact on oil price movements:
- Israel-Hamas War (Since October 2023): The outbreak of war in Gaza immediately led to a spike in oil prices due to fears of regional spillover. Although the conflict has not directly impacted the major oil-producing areas, the constant threat of escalation—especially involving Iran or its allied groups—adds to market uncertainty and risk premiums.
- Red Sea Crisis (Since November 2023): The Houthi movement’s attacks on commercial vessels in the Red Sea, including oil tankers, have disrupted global shipping lanes. As a result, many maritime companies—including those transporting oil—have had to reroute via the Cape of Good Hope. This leads to longer delivery times, higher transportation and insurance costs, and contributes to supply chain delays. Although a severe supply shortage has not yet materialized, the crisis continues to exert upward pressure on prices.
- Iran and Sanctions: Tensions surrounding Iran’s nuclear program and ongoing U.S. sanctions remain a key factor. Iran has managed to continue exporting oil, but any escalation or military confrontation could lead to a sharp reduction in Iranian supply, triggering a price surge in global markets.
- Strategic Chokepoints: The security of the Strait of Hormuz—one of the world’s most vital oil transit routes—remains a constant concern amid ongoing regional tensions. Any disruption in this area could lead to immediate and significant increases in oil prices.
OPEC+ Countries: Saudi Arabia and Russia as Key Players
The OPEC+ alliance, which unites the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) with its allies, has remained a key regulator of the global oil market from 2023 to the present. The alliance’s production decisions have a direct impact on oil prices and global energy security. Within this group, Saudi Arabia and Russia serve as dominant forces—whose cooperation and at times diverging interests often determine the market's direction.
Saudi Arabia's Role: Stabilization and Diversification
As the largest producer within OPEC and its de facto leader, Saudi Arabia plays a pivotal role in stabilizing the oil market. Since 2023, Riyadh has actively sought to maintain prices within a desired range to support its ambitious economic diversification program, Vision 2030.
- Voluntary Production Cuts: In 2023, amid global economic uncertainty, Saudi Arabia voluntarily reduced oil output to prevent a sharp price decline. This initiative was extended multiple times throughout 2024 and into early 2025, underscoring Saudi Arabia’s willingness to act as a "swing producer"—a country capable of adjusting supply quickly in response to market demand.
- Risk Management: Amid fears of escalating tensions between Israel and Iran, Saudi Arabia temporarily increased oil production by 600,000 barrels per day in June 2025 as a precautionary measure to mitigate potential supply disruptions. This additional output was directed toward domestic reserves rather than the open market, demonstrating a responsible and forward-looking approach.
- Market Share Strategy: Despite production cuts, Saudi Arabia has also sought to preserve or expand its long-term market share, particularly in Asia. As of August 2025, its oil exports to China reached a two-year high, highlighting Riyadh’s focus on maintaining influence in key growth markets.
Russia’s Role: Sanctions and the Pivot to Asia
Russia, as a major non-OPEC producer and co-leader of the OPEC+ framework, remains a critical player alongside Saudi Arabia. However, its position is complicated by extensive Western sanctions imposed after its invasion of Ukraine.
- OPEC+ Cooperation: Since 2023, Russia has actively coordinated with Saudi Arabia and other OPEC+ members to implement production cuts. That year, Russia reduced its oil production by 0.8%, fulfilling its alliance commitments—though some reports indicated occasional overproduction, sparking dissatisfaction among other members.
- Adaptation to Sanctions: Western sanctions—including a price cap on Russian oil exports—have posed serious challenges. Nevertheless, Russia has successfully redirected the majority of its oil exports to Asian markets, particularly China and India. To facilitate this, Moscow developed a "shadow fleet" of aging tankers designed to operate outside the purview of international monitoring mechanisms.
- Fiscal Dependence: Russia's economy remains heavily reliant on revenues from oil and gas exports, which incentivizes its government to support higher price levels and maintain production, despite logistical and regulatory obstacles.
OPEC+ General Direction
In 2023, OPEC+ implemented several rounds of production cuts to stabilize the oil market. Toward the end of 2024 and into early 2025, the alliance decided to gradually phase out these voluntary cuts, beginning a staged production increase in April 2025. This strategy offers flexibility and allows adjustments based on real-time market developments.
The group continues to hold monthly meetings to assess market conditions, monitor members’ compliance, and discuss compensation plans.
Despite differing geopolitical agendas, cooperation between Saudi Arabia and Russia remains central to OPEC+'s effectiveness. Their joint actions will continue to shape the trajectory of global oil prices and influence the balance of the international energy market.
Current Challenges in Middle Eastern Energy Policy
Since 2023, the energy policy landscape in the Middle East has faced several key challenges:
1. Regional Destabilization
Ongoing regional instability—most notably the Israel-Hamas conflict and the Red Sea crisis—continues to pose a constant threat to oil supply routes across the region. These tensions have also hampered major investment projects in energy infrastructure due to heightened political and security risks.
2. Global Energy Transition
Although short-term demand for oil remains stable, the long-term trajectory points toward a gradual global energy transition away from fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources. This shift will ultimately reduce demand for oil. While many Middle Eastern countries are investing in renewables, reducing oil dependency remains a slow and complex process, particularly for rentier economies deeply reliant on hydrocarbon revenues.
3. Influence of External Actors
Major global powers—such as the United States, China, and the European Union—continue to exert substantial influence over the region’s energy policies. Each seeks to secure stable energy supplies and protect their respective economic and strategic interests, contributing to a highly competitive and often fragmented geopolitical environment.
4. Domestic Economic Reforms
Oil-producing countries in the region are pursuing economic reform agendas aimed at reducing their dependence on oil revenues and diversifying their economies. These reforms require stable and predictable oil income to fund investments in non-oil sectors, making price volatility a key concern for policymakers.
Conclusion
From 2023 to the present, the oil market and energy policy in the Middle East have remained dynamic and fraught with complexity. Regional geopolitical tensions—particularly the Israel-Hamas conflict and the Red Sea crisis—have maintained upward pressure on oil prices by contributing to a persistent risk premium. In spite of global economic challenges, the OPEC+ alliance, led by Saudi Arabia and Russia, has managed to exercise some degree of market stabilization through coordinated production management.
Looking ahead, Middle Eastern energy policy will continue to be shaped by the intricate interplay of geopolitical developments, domestic economic reforms, and the ongoing global energy transition. Achieving peace and stability in the region is not only vital for the well-being of its populations, but also critical to ensuring the security and sustainability of global energy markets.